Vocabolario
Metalli
- stainless steel: steel that doesn’t need coating becase it doesn’t rust
- zinc: used to make brass (ottone - zinco e rame) and in galvanised coatings (zincatura) on steel
- iron: predominant metal in steel
- bronze: alloy made of copper (rame) and tin (stagno)
- tin: stagno
- lead: dense and poisonous metal - piombo
Legno
- hardwood: timber from deciduous trees - legno massello
- timber: legname
- softwood: timber from pine trees
- ore: rocks from which metals can be extracted - minerale grezzo
Adjectives
- toughness: the opposite of fragility
- abrasion resistance: resistance to damage caused by friction
- thermal stability: resistance to problems caused by temperature change
- lightweight: opposite of heavy
- durable: long-lasting
Tools
-
punch: makes holes by applying pressure to shear (sforzo di taglio) the material

-
abrasive wheel: has a hard, rough surface for cutting or grinding

-
guillotine: makes straight cuts by applying pressure to shear material

-
hole-saw: cuts a circular piece to remove an instact core of material ![[71brjyZBqcL.AC_SS450.jpg]]
-
kerf: the width of a saw cut
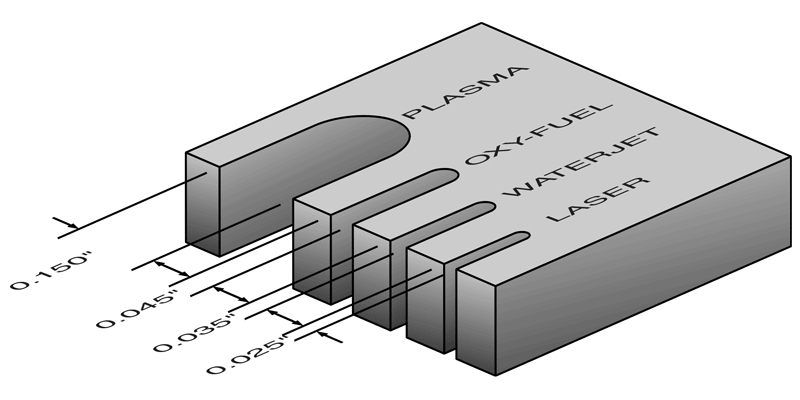
-
toothed blade: has sharp edges for cutting or milling

Views
- cross-section: gives a cutaway view of the joint between two panels
- elevation: gives a view of all the panels from the front
- exploded view: gives a deconstructed view of how the panels are fixed together
- note: gives a brief description or a reference to another related drawing
- plan: gives a view of the whole deck, from above
- schematic: gives a simplified representation of a network of air ducts
- specification: gives detailed written technical descriptions of the panels
Spaces
- confined spaces: small areas without ventilation
- co2 detector: measures carbon dioxide
- exposure: dangerous contact
- irritant: causes skin to react
- toxic: poisonous
- corrosive: burns the skin (or other material)
- flammable: catches fire easily
- naked flames/sparks: source of ignition
-
input: entry value, for example at the beginning of a process
-
output: exit value, for example at the end of a process
-
optimum: the best/most effective/efficient
-
differential: the gap between two values
-
consumption: the amount of supplies/fuel used
-
cumulative: the total quantity so far
-
rate: a value often expressed with per, for example units per hour
-
cycle: all the steps in a process, from start to finish
-
frequency: how often something happens
-
timescale: a specified period
-
continuous: without interruption
-
fluctuations: changes, movements in general
-
peaks and troughs: high points and low points on a graph curve
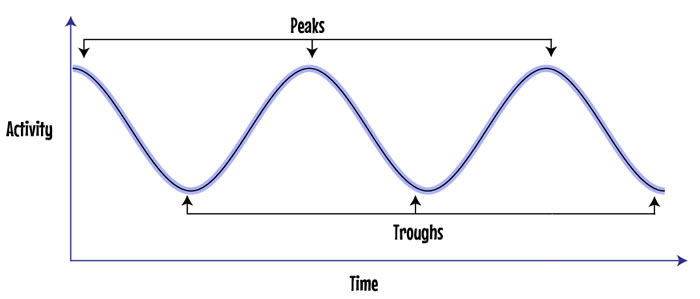
-
peak demand: maximum power requirement at a given time
-
range: amount between an upper and lower limit
-
band of fluctuation: zone of up-and-down movement
-
blips: momentary rises followed by a fall
-
continual: regular and repetitive
- appropriate/suitable: the right solution for a particular situation
- consistent/reliable: doesn’t break down, always perform in the same way
- cost-effective/economical: makes the most of resources, isn’t wasteful
- effective: performs a function well
- efficient: works quickly and well
- sufficient/adequate: good enough for the intended function